Making and Receiving Phone Calls
This introductory guide will show you how to make and receive calls from your own Node.js application.
Obtaining and configuring a number
Log in to your SignalWire Space. From the Phone Numbers section, you can buy a new phone number. You will need at least one number to make and receive calls. After you have acquired a number, open its settings by clicking on "Edit Settings". Scroll down until you reach "Voice and Fax Settings", as shown in the next figure, and configure it to:
- handle incoming calls using a Relay application,
- forward the call to the "office" Relay topic
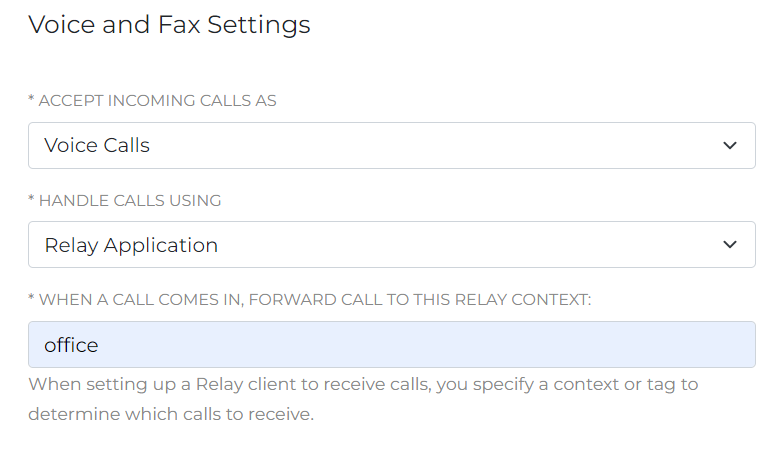
Voice configuration setting for handling incoming calls.
In Relay V4, a topic is a named scope that allows you to organize and categorize your resources. When you configure a phone number to handle calls with a Relay application and specify a topic, all calls to that number will be delivered to Relay clients listening on that topic.
Installation of the SDK
First, you need to obtain the Realtime SDK from npm. From your terminal you can run the following command to install it:
- npm
- Yarn
- pnpm
npm install --save @signalwire/realtime-api
yarn add @signalwire/realtime-api
pnpm add @signalwire/realtime-api
Then, include the package in JavaScript as follows:
import { SignalWire } from "@signalwire/realtime-api";
const voiceClient = client.voice;
Making your first call
To make a call from Node.js you need to instantiate a Voice client, and then call one of its dialing methods.
import { SignalWire } from "@signalwire/realtime-api";
const client = await SignalWire({
project: "your-project-id",
token: "your-api-token",
});
const voiceClient = client.voice;
try {
const call = await voiceClient.dialPhone({
from: "+1xxx", // Must be a number in your SignalWire Space
to: "+1yyy",
timeout: 30,
});
console.log("The call has been answered!", call.id);
} catch (e) {
console.error(e);
}
You also need to specify a Project ID and API token: find these in the API section of your space, as shown in the following figure. Make sure that your token has the "Voice" scope enabled.
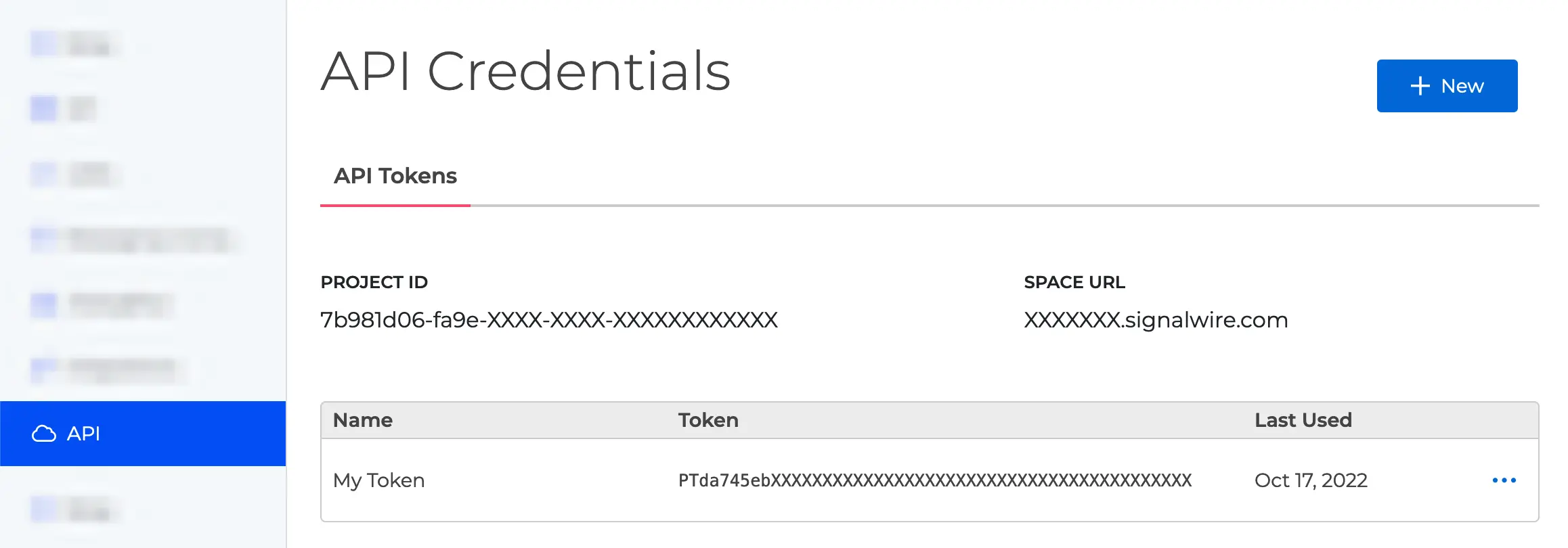
You can find your Project ID and Token from the API tab in your SignalWire Space. Make sure your token has the 'Voice' scope enabled.
Receiving incoming calls
Once a Client is initialized, you can listen for incoming calls on the selected topics (in our example, just "office"). For example:
await voiceClient.listen({
topics: ["office"],
onCallReceived: async (call) => {
console.log("Call received:", call.id, call.from, call.to);
try {
await call.answer();
console.log("Inbound call answered");
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error answering inbound call", error);
}
},
});
We used the "office" topic when listening to the voice client's events.
The topics array is used only listen to the phone numbers that you have
put in that specific topic from the SignalWire dashboard.
Your event handler receives a call object, which you can use to answer the call, to access fields such as call.from and call.to, or to call additional methods (playing audio, prompting for input, transferring the call, etc.)
Next steps
Congratulations! You can now make and receive calls with your Node.js application. You are now ready to explore the advanced guides in the Voice section from the left menu.